Firmware Documentation
Here you can find informations about updating firmware, changing boards properties and firmware revisions in the various versions of the robot.
FirmwareUpdater
With the FirmwareUpdater application it is possible to perform GUI-based FW update on both CAN- and ETH-based robots.
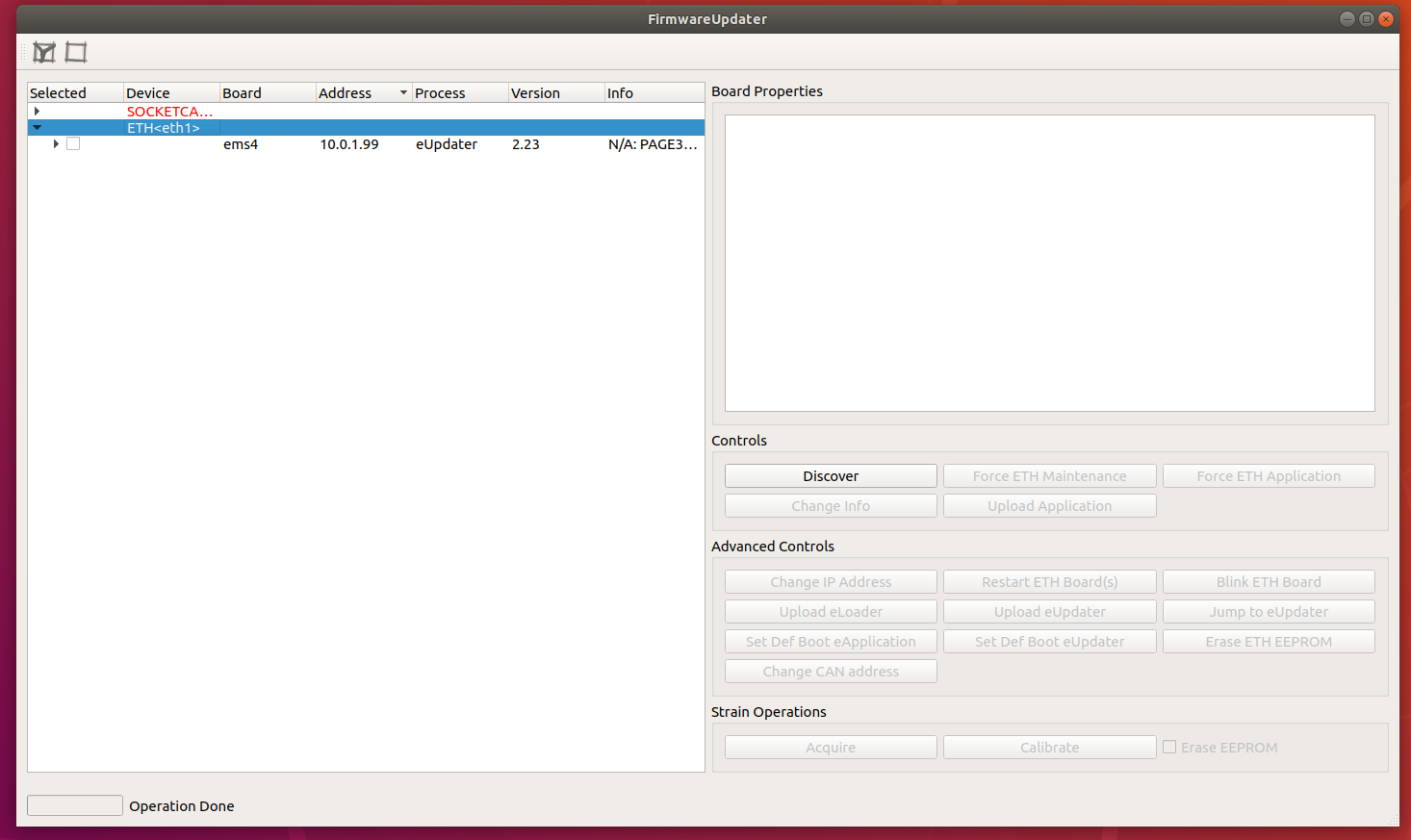
Firmware tools
With the FirmwareUpdater application it is possible to perform GUI-based FW update on both CAN- and ETH-based robots.
Here you can find quick and detailed instructions.
Operations on STRAIN with the FirmwareUpdater
The operations on the STRAIN boards described in the above sections can be performed also using the new FirmwareUpdater program.
With reference to Figure 2 inside this document you can do as follows.
- Upload a new FW using the button
Upload Application. See also section 6. - Tick the button
Erase STRAIN EEPROMand then upload the new FW if you also want to reset the F/T Sensors. - Launch the STRAIN Calibration GUI with the button
Calibrate STRAINif you want to import a calibration data file.
Firmware versions
A complete description of the different firmware versions used by the DSP boards which control the iCub robot can be found here
Automatic update of the robot
The user can also decide to perform the automatic update of the complete robot (or of some of its parts). Inside folder scripts of repository there are some examples.
The user can:
- retrieve info with scripts/FirmwareUpdater.script.info.all.sh,
- query the robot with scripts/FirmwareUpdater.script.verify.all.sh. This command also gives an estimate of the time required to perform the firmware update of the boards with old versions.
- update the firmware of all boards with old versions with scripts/FirmwareUpdater.script.update.all.sh
The topology of the robot
The robot network is described by the file network.{$YARP_ROBOT_NAME}.xml available for most robots in the repository. In case you cannot find this file, please ask for one here
In its inside there is thelist of all boards with their name, drive, address and link relations.
You can view some of this information with:
- scripts/FirmwareUpdater.script.info.all.sh: it prints the list of all boards with all details
- scripts/FirmwareUpdater.script.topology.all.sh: it prints the list of all ETH boards in link order.
Useful Resources
Below a list of useful links:
- Low-level boards programming (using degugger/programmer)
- Firmware sources
- Firmware binaries
FirmwareUpdaterdocFirmwareUpdatersources